Introduction
Have you ever thought about how a single device can bring someone back from the brink of death? That’s exactly what a defibrillator does! These amazing machines deliver a powerful shock that can get a stalled heart beating again. In this article, we’re going to explore the fascinating world of defibrillators, covering all the types, how they work, and why they’re so important. So, grab a cup of coffee and let’s get into it!
What is a Defibrillator?
At its core, a defibrillator is a device that sends an electric shock to the heart. This shock can correct an irregular heartbeat (arrhythmia) or restart the heart if it’s stopped. It’s like flipping a switch to bring a quiet room back to life.
Importance of Defibrillators in Medical Emergencies
Sudden cardiac arrest is a silent killer that can strike anytime, anywhere. Without immediate action, the chances of survival drop dramatically with each passing minute. Defibrillators step in to fill that crucial gap—buying precious time until professional help arrives. In fact, studies show that if a defibrillator is used within the first few minutes of cardiac arrest, survival rates can shoot up to 70%! That’s why you’ll find them in airports, schools, gyms, and even shopping centers.
Different Types of Defibrillators
Let’s break it all down so you can see what sets each type apart.
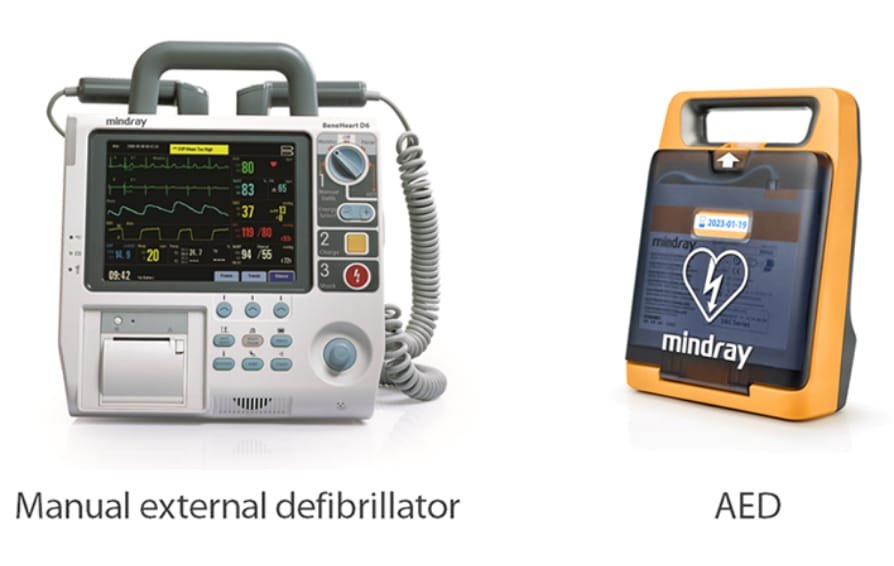
Automated External Defibrillators (AEDs)
Features of AEDs
AEDs are the go-to devices for emergencies in public spaces. They’re built to be super user-friendly—no medical degree required! They have:
- Voice prompts and images to guide you step by step.
- Lightweight, portable design.
- Pre-connected pads for quick application.
When to Use AEDs
AEDs are lifesavers in sudden cardiac arrest situations outside of hospitals. Picture this: someone collapses in a mall or at a concert. An AED can help anyone, from a bystander to a trained first aider, step in to save a life.
Real-World Impact of AEDs
AEDs aren’t just hypothetical solutions—they’re real-life heroes! There have been countless stories of ordinary people saving lives because an AED was close at hand. From office workers to high school athletes, AEDs have brought many people back from the edge of death.
Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillators (ICDs)
How ICDs Work
ICDs are like having a personal bodyguard for your heart. They’re implanted under the skin, usually near the collarbone, and have wires (leads) that run to the heart. These leads constantly monitor your heartbeat, and if something goes wrong, the ICD jumps into action to deliver a life-saving shock.
Who Needs an ICD?
ICDs are recommended for people with:
- A history of life-threatening arrhythmias.
- A previous cardiac arrest.
- Severe heart disease or weakened heart muscle.
Living with an ICD
Wearing an ICD doesn’t mean giving up on life. In fact, it can give you a new lease on it! People with ICDs can still work, travel, and enjoy their lives, knowing that help is always with them.
Wearable Cardioverter Defibrillators (WCDs)
Benefits of WCDs
WCDs are like temporary guardians. They’re worn over your clothes like a vest and provide continuous monitoring. If your heart starts to misbehave, they’ll deliver a shock without you needing to do a thing.
Limitations of WCDs
While WCDs are a great option for short-term protection, they’re not meant to be worn forever. They can be a bit bulky, and you’ll need to be diligent about wearing them 24/7—no skipping!
When WCDs Make Sense
WCDs are often used when someone is waiting for an ICD implant or recovering from a major heart issue. They’re the safety net that keeps you covered during those vulnerable times.
Manual External Defibrillators
Advanced Features for Medical Professionals
Manual defibrillators are what you see in hospitals and ambulances. They’re powerful tools with advanced settings like:
- Adjustable energy levels.
- Cardiac monitoring.
- ECG displays for rhythm interpretation.
Use Cases in Hospitals and EMS
These machines require trained professionals to operate. They’re used during cardiac arrests in hospitals, ambulances, and even on helicopters. Paramedics rely on them for quick, accurate intervention when every second counts.
Manual vs. Automated Defibrillators
Manual defibrillators offer more control, but they demand expertise. In contrast, AEDs are simpler and more intuitive—perfect for the average person in an emergency.
How Defibrillators Save Lives
Understanding Cardiac Arrest and Arrhythmias
A cardiac arrest doesn’t mean a heart attack (though the two are linked). During cardiac arrest, the heart’s electrical system goes haywire, causing the heart to quiver instead of pumping blood. This is called ventricular fibrillation. It’s like a car engine sputtering but never fully turning over.
How Defibrillators Restore Normal Heart Rhythm
The shock from a defibrillator is a controlled jolt that resets the heart’s electrical system. Picture your phone freezing—what’s the first thing you do? You restart it! That’s exactly what the defibrillator does for your heart.
Speed is Life
The faster you act, the better. For every minute without defibrillation, the chance of survival drops by 10%. That’s why having defibrillators in public places—and knowing how to use them—is so critical.
Choosing the Right Type of Defibrillator
Factors to Consider
Picking the right defibrillator depends on:
- User: Is it for laypeople or professionals?
- Location: Public places vs. hospitals.
- Medical needs: Are you at risk of sudden cardiac arrest?
- Budget: Different types come with different price tags.
Consultation with Healthcare Providers
If you’re considering a personal defibrillator like an ICD or WCD, always consult with your doctor. They’ll help you weigh the pros and cons based on your heart’s health.
Maintenance and Safety Tips for Defibrillators
Regular Inspections and Battery Checks
Your defibrillator is only helpful if it’s in working order. Most AEDs have indicator lights or alarms that let you know if something’s wrong. Check them monthly and after any use.
Replacing Pads and Batteries
Pads and batteries have a shelf life. Replace them as directed by the manufacturer—even if they look fine, expired pads might not stick properly.
Training and Education
Even though AEDs are simple, nothing beats a good training session. Learning CPR and AED use can give you the confidence to act fast in an emergency. Many communities offer free classes—check them out!
Stay Informed
Technology changes fast! Stay updated on the latest in defibrillator tech and guidelines. If you own a device, sign up for updates from the manufacturer.
Conclusion
Defibrillators are modern-day heroes, always ready to save a life. From the easy-to-use AEDs in public places to the life-saving ICDs tucked inside someone’s chest, each type has a vital role to play. Remember: these devices are only as good as the people who use them. So, whether you’re thinking about investing in a home defibrillator or just want to learn more, you’re already taking a step toward a safer, healthier future. Be prepared, stay informed, and you could be the difference between life and death for someone in need!
FAQs
How often should I check my defibrillator’s battery?
At least once a month! Check the status indicator and make sure the pads are still sealed and in date.
Can anyone use an AED?
Absolutely! AEDs are designed for anyone to use—no medical background needed.
Are there any risks associated with using a defibrillator?
When used correctly, the risks are minimal. The real risk is not using it when someone’s heart has stopped!
How do I know if I need an ICD?
Only a doctor can decide that. They’ll look at your heart health, your risk of arrhythmias, and your overall condition.
Do wearable defibrillators require a prescription?
Yes, WCDs are prescribed by a healthcare provider based on your specific heart health needs.

0 Comments